Abstract
Research Article
A Further Example Showing Efficiency of a Modeling Method Based on the Theory of Dynamic Systems in Pharmacokinetics
Maria Durisova*
Published: 25 January, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 007-012
Aims: To present a further example showing an efficiency of a modeling method based on the theory of dynamic systems in pharmacokinetics.
Study design:The goals of the current study were twofold: to present (1) a further example showing efficiency of a modeling method based on the theory of dynamic systems in pharmacokinetics, an to perform (2) a next step in tutoring the use of computational and modeling tools from the theory of dynamic systems in pharmacokinetics.
The data available in the study by Plusquellec et al. published in the October Issue of the Journal Medical Engineering & Physics were used to exemplify the method considered here. For modeling purpose an advanced mathematical modeling method was employed. Modeling was performed using the computer program named CTDB described in the study by Dedík et al. published in September 2007 issue of the Journal Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Main outcome: Modeling results revealed that computational and modeling tools from the theory of dynamic systems can be successfully used in the development of a mathematical model of such a complicated process as is a multiple sites discontinuous gastrointestinal absorption.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.hps.1001002 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Dynamic system; Mathematical model; Transfer function
References
- Dammann HG, Müller P, Kather H, Simon B. The new histamine H2-receptor antagonist ranitidine. Duration of action. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1981; 178: 151-154. Ref.: https://goo.gl/47Zy9Y
- Dawson J, Richards DA, Stables R, Dixon GT, Cockel R. Ranitidine --pharmacology and clinical use. J Clin Hosp Pharm Ther. 1983; 8: 1-13. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bkzNwF
- Eckardt VF, Cordes I, Janish HD, Wiemann H. Daytime acid secretion after a single dose of ranitidine and cimetidine--a double blind crossover study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984; 26: 177-182. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9HoAnV
- Brittain RT, Jack D. Histamine H2-antagonists--past, present and future. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1983, 5: 71-79. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EXuI0O
- Gaginella TS, Bauman JH. Ranitidine hydrochloride. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1983; 17: 873-885. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ptOQfC
- Merki HS, Witzel L, Walt RP, Neumann J, Scheurle E, et al. Comparison of ranitidine 300 mg twice daily, 300 mg at night and placebo on 24-hour intragastric acidity of duodenal ulcer patients. Aliment. Pharmacol Ther. 1987; 1: 217-223. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bEZhOc
- Plusquellec Y, Efthymiopoulos C, Duthil P, Houin G. A pharmacokinetic model for multiple sites discontinuous gastrointestinal absorption. Med Eng Phys. 1999; 21: 525-532. Ref.: https://goo.gl/BkULJt
- Reid SR, Bayliff CD. The comparative efficacy of cimetidine and ranitidine in controlling gastric pH in critically ill patients. Canad Anaesth. 1986; 33: 287-293. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Wcm42c
- Higuchi K, Watanabe T, Tominaga K, Shiba M, Nakagawa K, et al. Effects of ranitidine on quality of gastric ulcer healing compared with famotidine: a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2005; 25: 187-194. Ref.: https://goo.gl/i6D1S1
- Chrenova J, Durisova M, Mirciou C, Dedik L. Effect of gastric emptying and entero-hepatic circulation on bioequivalence assessment of. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 32: 413-419. Ref.: https://goo.gl/OanMbq
- van Rossum JM, de Bie JE, van Lingen G, Teeuwen HW. Pharmacokinetics from a dynamical systems point of view. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1989; 17: 365-392. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VAVsFe
- Dedík L, Ďurišová M. CXT-MAIN: a software package for the determination of the analytical form of the pharmacokinetic system weighting function. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 51: 183-192. Ref.: https://goo.gl/iAvtNQ
- Dedík L, Ďurišová M. Frequency response method in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokin Biopharm. 1994; 22: 237-307. Ref.: https://goo.gl/flpLxF
- Ďurišová M, Dedík L. Modeling in frequency domain used for assessment of in vivo dissolution profile. Pharm Res. 1997; 14: 860-864. Ref.: https://goo.gl/p6uWjQ
- Ďurišová M, Dedík L. A system-approach method for the adjustment of time-varying continuous drug infusion in individual patients: A simulation study. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2002; 29: 427-444. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1XtK6n
- Ďurišová M, Dedík L. New mathematical methods in pharmacokinetic modeling. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005; 96: 335-342. Ref.: https://goo.gl/UNFNoG
- Yates JW. Structural identifiability of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2006; 33: 421-439. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qf3HvZ
- Ďurišová M, Dedík L, Kristová V, Vojtko R. Mathematical model indicates nonlinearity of noradrenaline effect on rat renal artery. Physiol Res. 2008; 57: 785-788. Ref.: https://goo.gl/UW4Ees
- Ďurišová M. Physiologically based structure of mean residence time. Scientific World Journal. 2012. Ref.: https://goo.gl/DjpTgU
- Ďurišová M. A physiological view of mean residence times. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2014; 33: 75-80. Ref.: https://goo.gl/SFZu6S
- Ďurišová M. Mathematical model of pharmacokinetic behavior of orally administered prednisolone in healthy volunteers. J Pharmaceut & Pharmacol. 2014; 2: 1-5.
- Ďurišová M. Further worked out examples that illustrated the successful use of an advanced mathematical modeling method based on the theory of dynamic systems in pharmacokinetics. Int J Res Sci Res. 2015; 6: 4873-4879. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eB8xLo
- Ďurišová M. Mathematical model of pharmacokinetic behavior of warfarin. Adv Pharm Clin Trials. 2016; 1: 1-7. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1Zd7zi
- Ďurišová M. Computational analysis of pharmacokinetic behavior of ampicillin. J Appl Bioanal. 2016; 2: 84-89. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9uhDJ6
- Levitt DG. PK Quest: a general physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Introduction and application to propranolol. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 15: 2-5. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2UCayb
- Howell BA, Yang Y, Kumar R, Woodhead JL, Harill AH, et al. In vitro to in vivo extrapolation and species response comparisons for drug-indused liver injury (DILI) using DILsymTM: a mechanistic model of DILI. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2012; 39: 527-541. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LveVQu
- Dedík L, Ďurišová M, Penesová A, Miklovičová D, Tvrdoňová M. Estimation of influence of gastric emptying on shape of glucose concentration-time profile measured in oral glucose tolerance test. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2007; 77: 377-384. Ref.: https://goo.gl/0koO9F
- Ďurišová M. Physiologically based structure of mean residence time. The Sci World Journal. 2012. Ref.: https://goo.gl/xPqy08
- Ďurišová M. A physiological view of mean residence times. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2014; 33: 75-80. Ref.: https://goo.gl/44tImL
- Weiss M, Pang KS. Dynamics of drug distribution. I. Role of the second and third curve moments. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1992; 20: 253-278. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wiYtGU
- Verotta D. Concepts, properties, and applications of linear systems to describe distribution, identify input, and control endogenous substances and drugs in biological systems. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1996; 24: 73-139. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6lGcmI
- Xiao H, Song H, Yang Q, Cai H, Qi R,et al. A prodrug strategy to deliver cisplatin (IV) and paclitaxel in nanomicelles to improve efficacy and tolerance. Biomaterials. 2012; 33: 6507-6519. Ref.: https://goo.gl/UthCGZ
- Beckermann B, Kaliaguine V. The diagonal of the Padé table and the approximation of the Weyl function of second-order difference operators. Constr Approx. 1997; 13: 481-510. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AgA5a2
- Levy EC. Complex curve fitting. IRE Trans Automat Contr. 1959; 4: 37-43. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5g3G6d
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr. 1974; 19: 716-723. Ref.: https://goo.gl/KM0Sbt
- Lampariello F, Sciandrone M. Use of the minimum-norm search direction in a nonmonotone version of the Gauss-Newton method. J Optim Ther Appl. 2003; 119: 65-82. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JwG01Y
- Boyle P. Options: A Monte Carlo approach. J Fin Econom. 1977; 4: 323-338. Ref.: https://goo.gl/g8gMCC
- Varvel JR, Donoho DL, Shafer SL. Measuring of the predictive performance of computer controlled infusion pumps. J Pharmacokin Biopharm. 1992; 20: 63-84. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vsRmMu
- Siegel RA. Pharmacokinetic transfer functions and generalized clearances. J Pharmacokin Biopharm. 1986; 14: 511-521. Ref.: https://goo.gl/aRrc7I
- Segre G. The sojourn time and its prospective use in pharmacology.J Pharmacokin Bio- pharm. 1988; 16: 657-666. https://goo.gl/7yZs2V
- Yates JW. Structural identifiability of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2006; 33: 421-439. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VPEqJ0
- Rescigno A. Compartmental analysis and its manifold applications to pharmacokinetics. AAPS J. 2010; 12: 61-72. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qJ6h5r
- Gillespie WR, Veng-Pedersen P, Berg MJ, Schkottelius DD. Linear systems approach to the analysis of an induced drug removal process. Phenobarbital removal by oral activated charcoal. J Pharmacokin Biopharm. 1986; 14: 19-28. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vL520R
Figures:
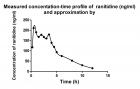
Figure 1
Similar Articles
-
A Further Example Showing Efficiency of a Modeling Method Based on the Theory of Dynamic Systems in PharmacokineticsMaria Durisova*. A Further Example Showing Efficiency of a Modeling Method Based on the Theory of Dynamic Systems in Pharmacokinetics. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hps.1001002; 1: 007-012
Recently Viewed
-
Pattern of Eye Disease in Nenwe Rural Eye Clinic, Nigeria: A Seven Year ReviewNnenna Maureen Ozioko*, Nkiru Mary Okoloagu, Emmanuel Sunday Onah, Catherine. Pattern of Eye Disease in Nenwe Rural Eye Clinic, Nigeria: A Seven Year Review. Int J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001056; 8: 004-015
-
Retinopathy of prematurity - Intersibling divergence of risk factors among twinsSudeep Navule Siddappa*,Kavitha Chikknayakanahalli Venugopal,Pavana Acharya ,Tintu Susan Joy . Retinopathy of prematurity - Intersibling divergence of risk factors among twins. Int J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001026; 4: 009-011
-
Effectiveness of levocetirizine in treating allergic rhinitis while retaining work efficiencyDabholkar Yogesh, Shah Tanush, Rathod Roheet, Paspulate Akhila, Veligandla Krishna Chaitanya, Rathod Rahul, Devesh Kumar Joshi*, Kotak Bhavesh. Effectiveness of levocetirizine in treating allergic rhinitis while retaining work efficiency. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001031; 7: 005-011
-
Hepatic Pseudolymphoma Mimicking Neoplasia in Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Case ReportJeremy Hassoun,Aurélie Bornand,Alexis Ricoeur,Giulia Magini,Nicolas Goossens,Laurent Spahr*. Hepatic Pseudolymphoma Mimicking Neoplasia in Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Case Report. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001115; 8: 152-155
-
Other Applications of Amniotic Membranes: Case SeriesLinda Guerrero*. Other Applications of Amniotic Membranes: Case Series. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001117; 8: 159-162
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."