Abstract
Research Article
Stepwise regression modeling on the monitoring of separation of Salvianolate through macroporous resin chromatographic column using UV spectral data
Yongsuo Liu*, Yong Wang and Guoan Luo
Published: 17 February, 2019 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-010
Aim: Study the monitoring method of separation of Salvianolate through macroporous resin chromatographic column using UV spectral data.
Method: HPLC was used to determine the concentration of Salviol B in the eluent liquid of macroporous resin chromatographic column. The UV spectrum of the eluent liquid was measured using portable UV spectrometer. Stepwise regression was used to develop the model to predict the concentration of Salviol B in the eluent liquid of macroporous resin chromatographic column using the UV spectral data.
Result: Stepwise regression model was developed to predict the concentration of Salviol B in the eluent liquid of macroporous resin chromatographic column. RMSE was 0.3263, MAP was 0.2323 and CV was 0.1796.
Conclusion: Stepwise regression model could be used to predict the concentration of Salviol B in the eluent liquid of macroporous resin chromatographic column using UV spectral data
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001012 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Stepwise regression model; UV spectrum; Variable selection; Optimization
References
- Zhang H, Zhang Y, Yang R, Li YJ, Wang M, et al. Correlation study on effects of salvianolate on inflammatory cytokines of patients with acute coronary syndrome. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med. 2013; 33: 598-601. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2X8V6P
- Jian J, Yingmin L, Nengcai YAO, Cunfang DOU, Cenchang Y, et al. Study of depside salt from salvia miltiorrhiza's effect on coronary slow flow phenomenon. J Clin Cardiol (China). 2011; 27: 751-752. Ref.: https://goo.gl/3QxH6B
- Yang HH, Qin F, Liang QL, Wang Y, Wang YM, et al. LapRLSR for NIR spectral modeling and its application to online monitoring of the column separation of Salvianolate. Chin Chem Lett. 2007; 18: 852-856. Ref.: https://goo.gl/he5qub
- Jin HY, Chen LG, Zhou XQ, Zhang SQ, Liu QW. On-line Monitoring of Dynamic Microwave-assisted Extraction of Scutellarin from Scutellaria barbata by UV Spectroscopy. J Jilin Univ (Sci. Edit.). 2009; 47: 1313-1317. Ref.: https://goo.gl/23bCcQ
- Sun NZ, Yang SL, Yeh WWG. A proposed stepwise regression method for model structure identification. Water Resour Res. 1998; 34: 2561-2572. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JWSJtj
- Liao XT, Li Q, Yang XJ, Zhang WG, Li W. Multiobjective optimization for crash safety design of vehicles using stepwise regression model. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2008; 35: 561–569. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XzpTqX
- Lachniet MS, Patterson WP. Use of correlation and stepwise regression to evaluate physical controls on the stable isotope values of Panamanian rain and surface waters. J Hydrol. 206; 324: 115–140. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bFQLu3
- Oros G, CserhAti T, Forgks E. Use of spectral mapping and stepwise regression analysis for the assessment of the relationship between chemical structure and biological activity of surfactants. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 1997; 39: 95-101. Ref.: https://goo.gl/kS5P6Q
- Zhou N, Pierre JW, Trudnowski D. A stepwise regression method for estimating dominant electromechanical modes. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012; 27: 1051-1059. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Hczrs7
- Jang CS, Youn BD, Wang PF, Han B, Ham SJ. Forward-stepwise regression analysis for fine leak batch testing of wafer-level hermetic MEMS packages. Microelectron Reliab. 2010; 50: 507-513. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rm6oDF
- Telmo C, Lousada J, Moreira N. Proximate analysis, backwards stepwise regression between gross calorific value, ultimate and chemical analysis of wood. Bioresour Technol. 2010; 101: 3808-3815. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8SwLVV
- Templ M, Kowarik A, Filzmoser P. Iterative stepwise regression imputation using standard and robust methods. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2011; 55: 2791-2806. Ref.: https://goo.gl/w5ZgQN
- Willmott CJ, Matsuura K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Int J Clim Res. 2005; 30: 79-82. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7jBiMe
- Huang C, Townshend JRG. A stepwise regression tree for nonlinear approximation: applications to estimating subpixel land cover. Int J Remote Sensing. 2003; 24: 75–90. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8sfukP
- Ssegane H, Tollner EW, Mohamoud YM, Rasmussen TC, Dowd JF. Advances in variable selection methods Ⅰ:causal selection methods versus stepwise regression and principal component analysis on data of known and unknown functional relationship. J Hydrol. 2012; 438-439: 16-25. Ref.: https://goo.gl/53wLeh
- : https://goo.gl/Kf3cwW
- : https://goo.gl/42QkFw
- Malek MH, Berger DE, Coburn JW. On the inappropriateness of stepwise regression analysis for model building and testing. Eur J Appl Phsiol. 2007; 101: 263-264. Ref. https://goo.gl/PZBNp3
Figures:
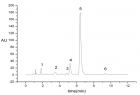
Figure 1
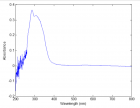
Figure 2
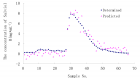
Figure 3
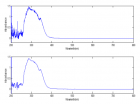
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
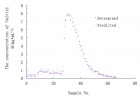
Figure 7
Figure 8
Figure 9
Similar Articles
-
Stepwise regression modeling on the monitoring of separation of Salvianolate through macroporous resin chromatographic column using UV spectral dataYongsuo Liu*,Yong Wang,Guoan Luo. Stepwise regression modeling on the monitoring of separation of Salvianolate through macroporous resin chromatographic column using UV spectral data. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001012; 3: 001-010
-
Design and optimization of mRNAs encoding an Anti-TIGIT antibody with therapeutic potential for cancer in TIGIT-humanized BALB/c MiceJingmin Cui, Gulisaina Qiaerxie, Hui Qin, Feng Long, Xi Wang, Zhixin Yang, Peng Du*, Yong Cui*. Design and optimization of mRNAs encoding an Anti-TIGIT antibody with therapeutic potential for cancer in TIGIT-humanized BALB/c Mice. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001038; 7: 008-016
-
Beta-1 Receptor (β1) in the Heart Specific Indicate to StereoselectivityRezk Rezk Ayyad*, Ahmed Mohamed Mansour, Ahmed Mohamed Nejm, Yasser Abdel Allem Hassan, Norhan Hassan Gabr, Ahmed Rezk Ayyad. Beta-1 Receptor (β1) in the Heart Specific Indicate to Stereoselectivity. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001060; 8: 082-088
Recently Viewed
-
The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution StudyMansouri Nada1, Yaiche Rahma*, Takout Khouloud, Gargouri Faten, Tlili Karima, Rachdi Mohamed Amine, Ammar Hichem, Yedeas Dahmani, Radhouane Khaled, Chkili Ridha, Msakni Issam, Laabidi Besma. The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution Study. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001041; 8: 006-011
-
Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health PracticesAlya Algamdii*. Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health Practices. Clin J Nurs Care Pract. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001059; 9: 007-011
-
Multipurpose Antioxidants based on Food Industry Waste: Production and Properties EvaluationToshkhodjaev*. Multipurpose Antioxidants based on Food Industry Waste: Production and Properties Evaluation. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001062; 9: 001-003
-
Relationship between Fertility Diet Score Index Items and Ovulation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Narrative ReviewHadis Alimoradi,Faezeh Mashhadi,Ava Hemmat,Mohsen Nematy,Maryam Khosravi,Maryam Emadzadeh,Nayere Khadem Ghaebi,Fatemeh Roudi*. Relationship between Fertility Diet Score Index Items and Ovulation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001061; 8: 041-048
-
Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in SenegalMoustapha Mbow*,Ibrahima Diallo,Mamadou Diouf,Marouba Cissé#,Moctar Gningue#,Aminata Mboup,Nafissatou Leye,Gora Lo,Yacine Amet Dia,Abdou Padane,Djibril Wade,Josephine Khady Badiane,Oumar Diop,Aminata Dia,Ambroise Ahouidi,Doudou George Massar Niang,Babacar Mbengue,Maguette Dème Sylla Niang,Papa Alassane Diaw,Tandakha Ndiaye Dieye,Badara Cisé,El Hadj Mamadou Mbaye,Alioune Dieye,Souleymane Mboup. Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in Senegal. Int J Clin Virol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001041; 6: 001-006
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."